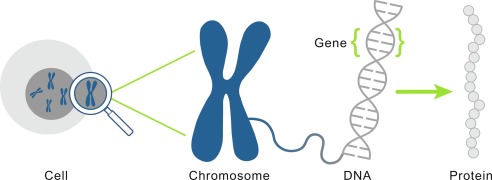
Genes are the building blocks of heredity. They hold the DNA, the instructions for making protein. Proteins are responsible for moving molecules from one place to another in the cell, they build structures, break down toxins and do some other maintenance job in the cell.
Genetic Disorders can be a result of genetic abnormalities such as gene mutation or additional chromosomes.
There are about 6,000 known genetic disorders.
Mitchondria are small particles within cells. The mitochondrial DNA is always inherited from the female parent.
Chromosomes are structures that hold genes.
Mutation is a change in a gene or genes which can happen during one’s lifetime or is inherited.
Genetic Disorder occurs when mutation changes the gene’s instructions for making a protein, so the protein does not work properly or is missing entirely.
There are many types of genetic disorders, but the common 3 are:
Single Gene Disorder: This is when the mutation affects one gene e.g sickle cell anemia
Chromosomal Disorder: This is when chromosomes (or parts of chromosome) are missing or changed e.g down syndrome
Complex Disorder: This is when the mutation occurs in two or more gene e.g colon cancer
To learn more, we invite you to register for our Open Conversation where we will be “Addressing the Barriers against Health-related Disabilities” and promoting various organisations that help promote awareness, care and research on genetic disorders.

